Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-04-21 Origin: Site









Installing shielded cable glands is a key step in building safe and interference-free electrical systems. These compact connectors not only secure cables mechanically but also protect sensitive circuits from electromagnetic interference (EMI), dust, moisture, and strain. When installed correctly, they create a grounded path that shields cables and enclosures from signal distortion and performance issues. Used in industries like telecommunications, energy systems, smart vehicles, and industrial automation, proper installation ensures system reliability and long-term safety. This guide explains everything you need—tools, preparation, step-by-step process, and expert tips—to install shielded cable glands the right way, every time.
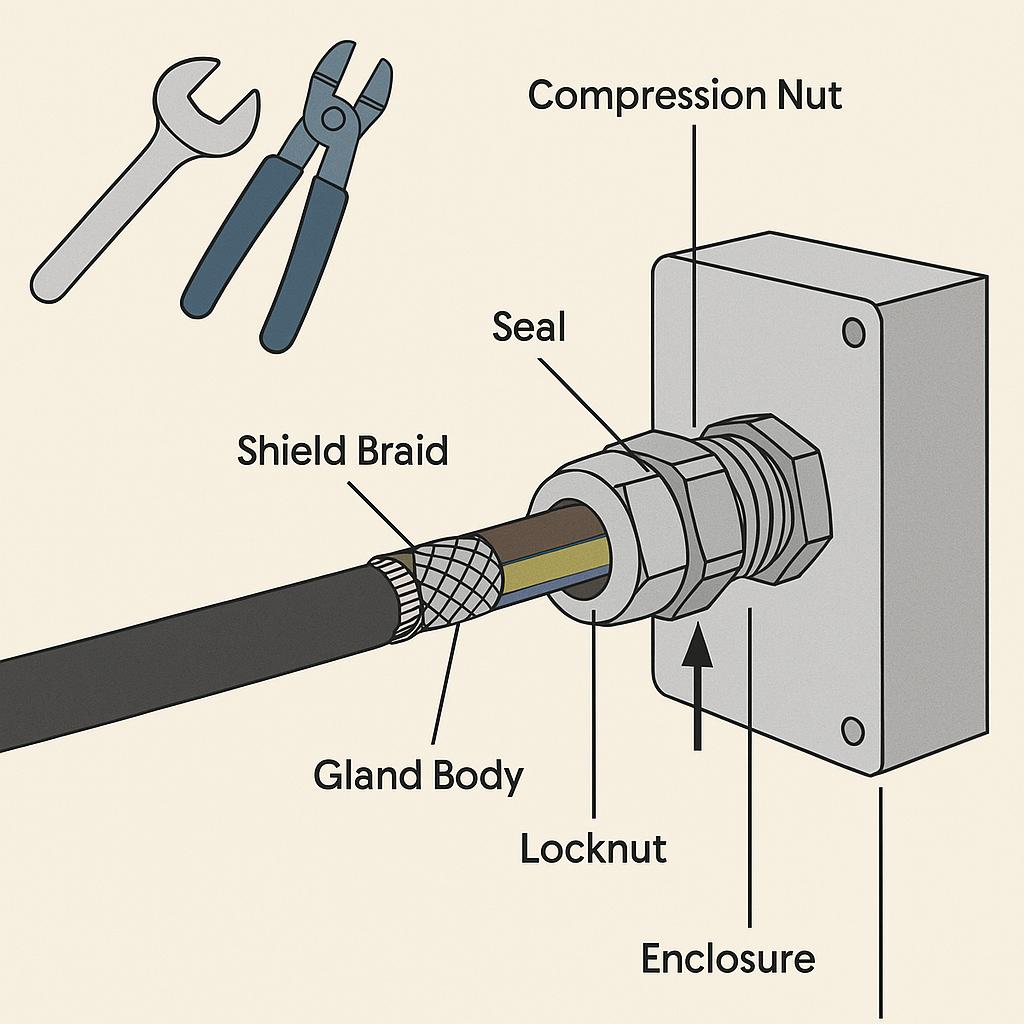
A shielded cable gland is more than a fastener—it’s a multifunctional safety component. It holds the cable firmly in place, creates an airtight and watertight seal, and grounds the cable’s shield. This stops EMI from disrupting system operations. In high-performance applications like EV systems, high-speed data centers, or offshore wind turbines, failure to install cable glands correctly can result in costly outages, signal loss, and even equipment damage.
That’s why proper cable gland installation for shielded cable isn't optional—it’s essential. Brands like HUNTEC manufacture EMC-rated, IP68-protected shielded glands designed for fast and secure installation. But even the best products won’t perform as intended unless they’re installed properly.
To install a shielded cable gland, gather the following items:
| Tool or Material | Function |
|---|---|
| Spanner / Wrench | Tighten the gland into enclosure or panel |
| Wire stripper | Remove outer jacket without damaging inner layers |
| Torque wrench | Apply correct tightening force |
| Thread sealant | Optional, improves water resistance in outdoor use |
| Screwdriver | Terminal connection if grounding needed |
| Grounding tester | Confirm shield-to-body continuity |
In most cases, only hand tools are needed. But for industrial setups, using a torque wrench ensures seal reliability and prevents over-tightening.
Before you install, know your cable and gland type:
Is the cable foil-shielded, braid-shielded, or unarmored?
What is the outer diameter of the cable?
Is the gland thread metric, NPT, PG, or BSP?
What is the IP rating requirement (e.g., IP66, IP68)?
Do you need EMI protection or flameproof performance?
Shielded cable glands are usually used with braided or foil-shielded cables to provide grounding. Choosing the wrong type can lead to electrical issues or mechanical failure.
Choose a gland that matches the outer cable diameter and shield type. Ensure the gland is labeled EMC cable gland or shielded cable gland for EMI protection. The gland thread must also fit the enclosure or junction box.
Unscrew the gland into its components:
Compression nut
Seal insert
Shield contact ring or spring
Gland body
Locknut and washer (if included)
Place them on a clean surface for easy access.
Strip the outer jacket of the cable.
Leave about 15–20mm of shield braid or foil exposed.
Be careful not to damage the braid or cut into the core insulation.
Fold the braid evenly around the outer jacket to ensure full 360° contact inside the gland.
Slide the cable through the compression nut and seal insert.
Make sure the exposed shield touches the contact element.
Align it without twisting.
In some models, the shield fits between a cone and sleeve to form a conductive path.
Screw the gland body into the enclosure panel or housing.
Then, tighten the compression nut by hand, followed by a wrench.
Use a torque wrench if torque values are specified (common in IP68 glands).
Ensure the gland forms a snug seal around the jacket and that the shield is grounded.
Use a continuity tester or multimeter.
Touch one probe to the gland body and the other to the cable shield.
A continuous beep or reading confirms proper grounding.
Use IP68-rated shielded glands with corrosion-resistant metal (e.g., nickel-plated brass or stainless steel).
Apply thread sealant or O-rings to prevent water ingress.
Choose low-profile or right-angle shielded cable glands.
Swivel-thread models allow easier positioning in tight spaces.
Use glands that support multi-hole inserts or hybrid EMC designs.
Label cables clearly after installation to avoid confusion.
| Mistake | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Using the wrong gland size | Loose fit, poor EMI shielding |
| Damaging cable shield during strip | Loss of continuity, weak grounding |
| Over-tightening the compression nut | Crushed cable or broken seal |
| Poor alignment of braid to contact | No shield connection, EMI leaks |
| Skipping continuity testing | Hidden installation failures |
| Using standard gland for EMI needs | System-level signal disruption or failure |
Avoiding these mistakes ensures that your shielded cable gland works as expected and extends the life of your equipment.
| Installation Step | Task | What to Watch For |
|---|---|---|
| Select Gland | Match cable diameter and thread type | Gland should support cable shield |
| Prepare Cable | Strip jacket and fold shield | Don’t cut shield strands |
| Disassemble Gland | Lay out all parts | Ensure nothing is missing or damaged |
| Insert and Align | Position shield with contact ring | Shield must make full contact |
| Tighten and Seal | Apply torque to secure gland | Avoid leaks and over-tightening |
| Test Connection | Check continuity between gland and shield | Use a multimeter for accuracy |
| Material | Benefit | Application Area |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel-plated brass | High conductivity, corrosion resistance | Telecom, industrial automation |
| Stainless steel | Strong, durable, rust-proof | Marine, chemical plants |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, good for mobile systems | EVs, robotic arms |
| Plastic with EMI insert | Low-cost indoor EMI shielding solution | Office networks, indoor panels |
HUNTEC’s shielded cable glands are made from premium-grade brass with anti-oxidation surface treatment, ensuring both performance and durability across environments.
Tool-free installation designs are on the rise, improving assembly speed.
Compact EMC cable glands allow integration into tighter spaces.
Some glands now include built-in surge suppression or smart ID tags.
Halogen-free materials meet eco-regulations in new electrical systems.
Shielded glands are increasingly used in consumer electronics with embedded antennas or IoT devices.
Installing shielded cable glands correctly is essential to protect systems from EMI, water, and strain. A good installation keeps your signal strong, your gear safe, and your maintenance costs low. Whether you're wiring a telecom tower, automating a factory, or building a smart vehicle, the right gland makes the difference.
With a full range of reliable, performance-tested products, HUNTEC delivers shielded cable gland solutions you can count on for every application—from clean rooms to offshore rigs.
A: They ground the cable shield, diverting electromagnetic interference away from the circuit.
A: No. Only shielded cable glands ensure proper grounding and EMI protection.
A: Yes. A continuity test confirms shield grounding and avoids hidden faults.
A: Yes. Many are IP66/IP68 rated and block both EMI and environmental hazards.